Family:
Myrtaceae
Eucalyptus bicostata
Eurabbie
(syn. E. globulus subsp. bicostata)
Other Names: Blue Gum.
First Nations Name(s):
Name Origin:
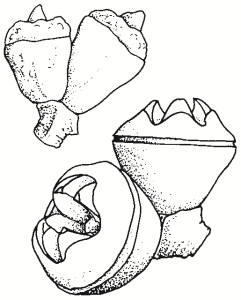
bicostata — from the Latin bi, two, plus costatus, ribbed, referring to the two ridges commonly on the buds and fruits.
Regional Subspecies:
Occurrence:
Regional:
Primarily in wetter areas east of Hume Highway and south of Murrumbidgee catchments.
Australia:
NSW, Vic.
Habitat:
Fertile soils in sheltered areas, in wet forest.
Habit:
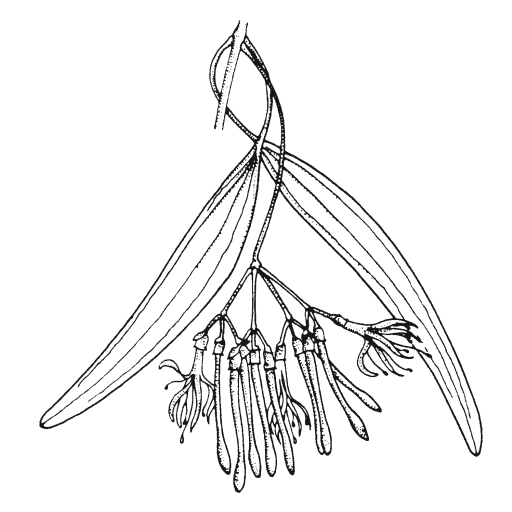
Tree to 40 m high with smooth white or grey bark, shedding in ribbons, and long narrow glossy green adult leaves.
Site Preference:
Moist, relatively heavy, fertile soil. Tolerates poorly-drained and boggy soil. Seedlings are susceptible to frost.
Characteristics:
Grows very rapidly when young. Uses large volumes of water, and if grown outside its natural range, summer water shortages may lead to tree death. Responds to fertiliser.
Flowering:
White-cream, Sep-Jan.
Seed Collection:
Early Jan to late May.
Propagation:
From seed (± 109 viable seeds per gram). Optimum germination temperature 27°C.
Regeneration:
From seed, under during favourable seasons such as wet summers, particularly in absence of competitive exotic grasses. Coppices after fire or cutting.
VALUES:
Shade & Shelter:
Useful high-level cover in windbreaks. Casts heavy shade which suppresses most other vegetation.
Land Protection:
Useful in gully erosion control, behind fibrous-rooted understorey plants.
Wildlife:
Nectar-rich flowers food for various insects and nectar-feeding birds. Fruit and seeds eaten by lorikeets, parrots and rosellas. Foliage important koala food. Hollows nesting sites for many birds and mammals. Important food source for the Yellow-bellied Glider.
Fuel:
Moderate. Forms good coals and few sparks. Rates fair in splitting and ignitability.
Timber:
Strong, moderately durable, with light-yellow or brown heartwood. Usually has interlocked grain with distinct growth rings. Density about 900 kg/m3. Mainly used in general construction, for making tool handles, and in bridges. Was used for cross-arms in electricity poles. Increasingly used as feature timber. Sapwood susceptible to damage by Lyctus borers. Can be grown for hardwood pulp or sawlogs. Useful as quick-growing ‘nurse’ crop for Blackwood (Acacia melanoxylon) which benefits from shelter.
Ornamental:
Useful in parklands where a dense stand required quickly. Generally unsuitable for smaller gardens. Sometimes seen as untidy because its fallen leaves and twigs are slow to decompose. Suppresses most other vegetation.
Other:
Leaves were used in a range of treatments including croup, asthma and colds as a vapour inhalation, and as an insecticide powder or spray. Leaves produce orange-tan dye with mordant alum.